Building Africa’s Capacity for Cholera Surveillance and Outbreak Response
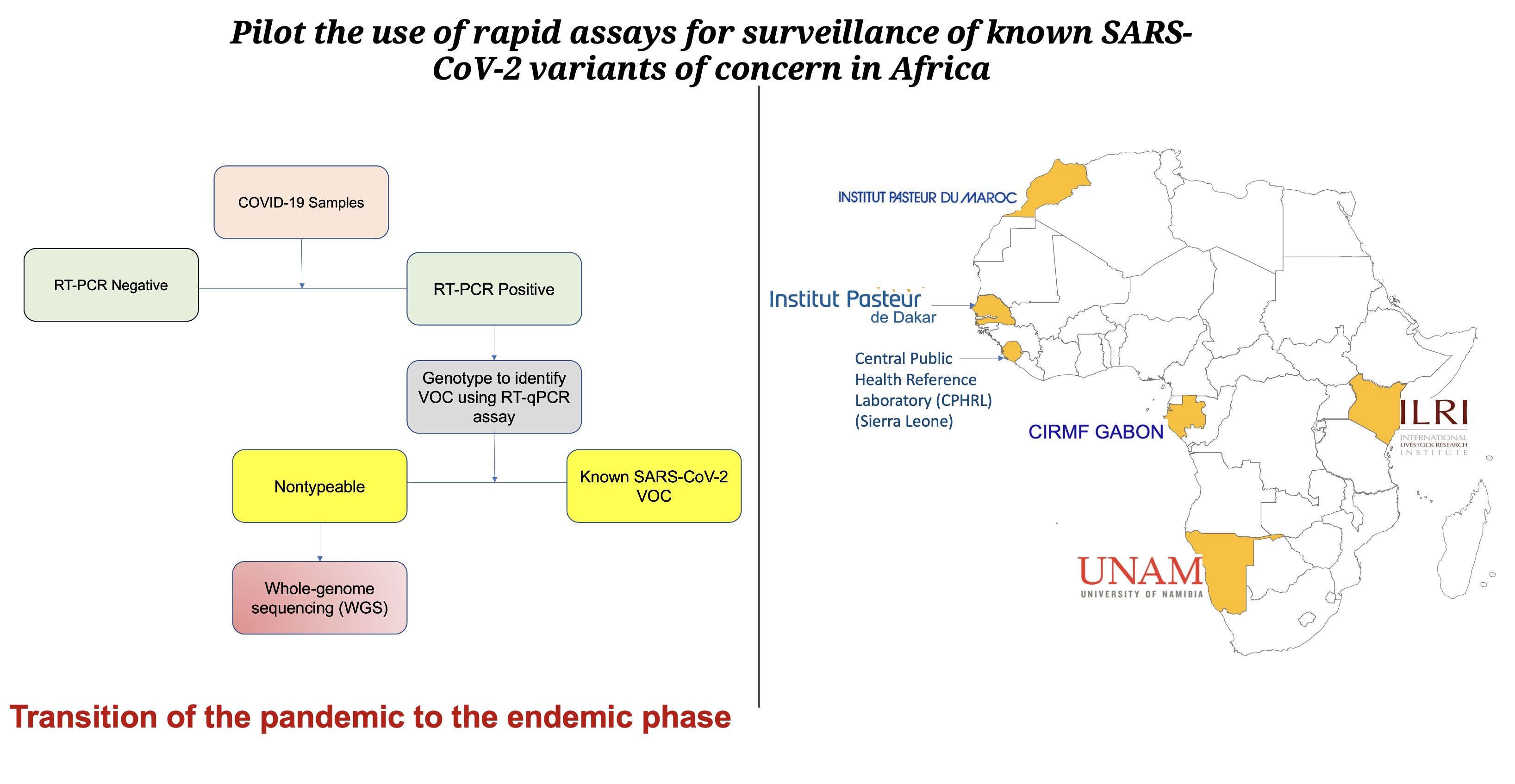
Establishing capacity for cholera genomic surveillance in Africa.
CholGen: Building Capacity for Genomic Surveillance of Cholera in Africa
Cholera remains a significant public health challenge across Africa, with periodic outbreaks causing considerable morbidity and mortality. The CholGen project aims to strengthen genomic surveillance capacity for cholera in Africa, addressing the critical need for rapid, data-driven public health interventions. By leveraging advancements in pathogen genomics, CholGen seeks to enhance understanding of cholera dynamics, improve outbreak response, and support long-term control strategies.
Project Resources
CholGen GitHub – Vibecheck
CholGen Publication – Nature Communications
Project Progress
You can access a detailed overview of CholGen activities here.
Project Goals
The primary objective of CholGen is to build and expand the capacity of laboratories and public health institutions across Africa to perform genomic surveillance of Vibrio cholerae, the causative agent of cholera. The project focuses on equipping regional labs with the tools, infrastructure, and expertise necessary to sequence, analyze, and interpret genomic data. This capacity will enable the timely identification of cholera strains, their origins, transmission pathways, and potential antimicrobial resistance patterns.
Approach
CholGen collaborates with National Public Health Institutes (NPHIs) and regional laboratories, providing specialized training in whole-genome sequencing (WGS) and bioinformatics. By utilizing cutting-edge genomic tools, the project supports routine surveillance and rapid response during outbreaks. CholGen also emphasizes partnerships, fostering collaboration between African countries to share data and resources for regional cholera control.
Expected Outcomes
🔹 Enhanced Genomic Surveillance:
Development of a sustainable genomic surveillance network capable of tracking cholera outbreaks
in real-time.
🔹 Data-Driven Interventions:
Improved understanding of cholera transmission dynamics and hotspots, informing targeted
interventions.
🔹 Capacity Building:
A skilled workforce proficient in genomic technologies, ensuring long-term sustainability of
cholera surveillance efforts.
🔹 Policy Support:
Evidence-based insights to guide regional and national cholera control strategies.
CholGen represents a critical step towards combating cholera in Africa, empowering countries to respond effectively to outbreaks and move closer to eliminating this deadly disease. By combining technology, expertise, and collaboration, the project contributes to building resilient health systems and saving lives.